Mole Removal
Mole Removal
Changes in skin color are common and usually harmless. Skin color is determined by melanin, a protein made by cells called melanocytes. Darker skin has a higher concentration of melanin; light skin has less. Your melanin level is genetically determined, but exposure to the sun also plays a major role. In an effort to protect skin from the sun’s harmful ultraviolet rays, melanin levels increase, darkening the skin.
Increase in Pigment
Several conditions can cause darker areas of skin:
Melasma is a condition in which dark areas appear on the cheeks, forehead, and above the lips. It can be caused by the hormonal changes of pregnancy or menopause and by taking oral contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy. Melasma usually fades when hormones stabilize.
Liver Spots, also called age spots, are darkened spots that often occur on the hands and other sun-exposed areas. They arise when aging skin becomes more fragile and more vulnerable to the sun’s ultraviolet light. Areas of the skin exposed to perfumes or scented cosmetics along with sunlight can also temporarily become darker.
These conditions may be bothersome but are not harmful. Other increases in pigment may warrant your doctor’s attention. Skin that seems to tan without being exposed to the sun may be a sign of an underlying disease, such as Addition disease or Cushing disease. Moles can also occur or change due to exposure to sunlight. Consult your doctor about any change in a mole so that he or she can rule out cancer.
Decrease in Pigment
Vitiligo causes patches of skin to become lighter. In vitiligo, parts of the skin stop producing melanin. The result is symmetrical white patches that often occur on the face, hands, armpits, and groin. In some people, the patches begin producing pigment again without treatment. The cause of vitiligo is not known, but it may be an autoimmune disorder that affects melanocytes, the cells responsible for making pigment.
Albinism is a rare, inherited disease in which melanin, which colors the skin, hair, and eyes, is absent from birth. People with albinism have extremely pale skin and hair and often have eye problems, including extreme sensitivity to sunlight.
Phenylketonuria, a genetic condition, causes lower melanin levels and fairer, but not white, skin and hair
Psoriasis and other scaly skin conditions may leave the skin melanin-deficient after treatment to remove scales.
Tinea versicolor may bring on a similar lack of pigment.
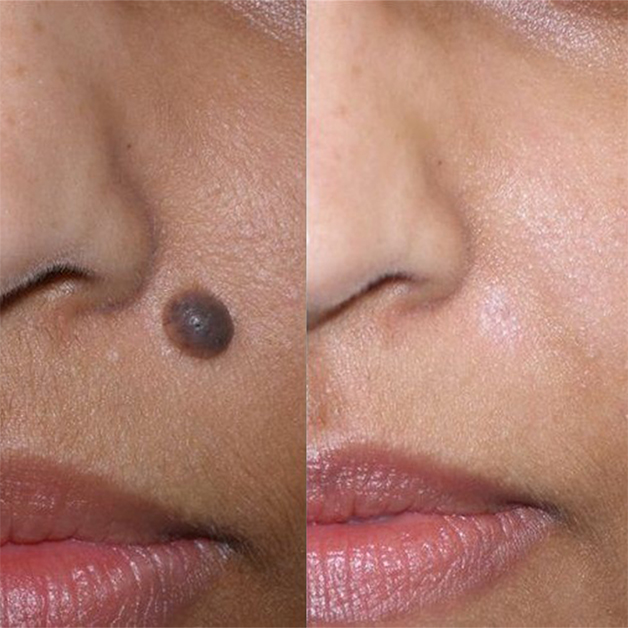
Treatment Options
Normal pigmentation gradually reappears when psoriasis or tinea versicolor are effectively treated. Depigmenting creams can help lighten dark areas in other conditions, although they should be applied carefully since they lighten normal skin as well. For vitiligo and age spots, you can also cover areas of increased or decreased pigmentation with a cosmetic. Your doctor may recommend psoralen, a drug that makes skin more sensitive to light, and ultraviolet light (in combination called PUVA) for vitiligo. The drug tretinoin in cream form may help lighten the skin discoloration of melasma. At our facility the photorejuvenation procedure is available to lighten dark patches of skin. Depending on the specific case a combination of chemical peel and laser photorejuvenation may be the preferred choice. During the consultation session we will be able to recommend the most suitable procedure for your condition.
